Practical guide to bug management (tools, tips, & getting started)
You can’t stop every bug from happening, but you can control how you handle them when they show up and manage where you capture them, how you prioritize them, who owns them, and whether your team learns from them.
When that control is missing, though, bugs wind up across half-finished Jira tickets, scattered Slack threads, screenshots in emails, and spreadsheets that no one trusts anymore. This results in slower delivery, frustrated teams, and avoidable rework.
Overall, effective bug management isn’t about finding the “perfect” tool—it’s about supporting bugs’ full lifecycle with modern systems that help you keep context connected, decisions clear, and teams aligned.
What is bug management?
A “report a bug” template in Notion (Source)
Bug management is the process of identifying, triaging, prioritizing, fixing, and learning from bugs. Many teams think of bug management as issue tracking, but that’s only one part of the process. Successful bug management also includes these steps:
Capturing complete, actionable bug reports
Evaluating their impact and severity
Prioritizing bugs alongside feature development
Coordinating fixes across teams
Closing the loop with learnings that prevent repeat issues
When bug management works well, bugs don’t derail project management roadmaps or dominate standups. They instead become part of a predictable, transparent system that helps you ship better software over time.
Common types of bugs
While bugs can take many forms, software development teams often encounter these recurring categories:
Functional bugs: Features or functionality that don't work as teams intended or break under specific conditions (like a login button that fails)
UI and UX bugs: Visual inconsistencies, layout issues, or confusing interactions that degrade the user experience (like vague error messages)
Performance bugs: Software defects that create inefficiency (like slow load times, excessive memory usage, or timeouts that impact reliability)
Integration bugs: Failures where systems, open-source APIs, or third-party tools don’t communicate properly
Regression bugs: Issues that resurface after resolving bugs, often due to changes elsewhere in the codebase
Each type of bug comes with different levels of urgency and context. As a result, managing them well often requires more than a simple issues report.
The challenges of bug management
Bug management challenges are common and often stem from disconnected tools and workflows that don’t naturally work together. Here are some common examples:
Scattered context: Teams might store bug reports in Jira, logs in a shared folder, and decisions in chats. This scattered context makes it hard to know where a resolution stands.
No single source of truth: Often, teams use multiple systems with overlapping or outdated information.
Duplicate bugs: The same issue might have multiple reports in place because there’s no visibility into which bugs already exist.
Vague severity definitions: “High priority” often means different things to different people.
Poor cross-team visibility: Product, design, and support might not know what other teams are working on or why.
Having a connected workspace where bugs, discussions, decisions, and timelines live together removes much of this friction. And on top of that, adding in AI to organize, summarize, and surface insights makes addressing bugs far more manageable.
What are the benefits of effective bug management?
A bug tracker template in Notion (Source)
When bug management improves, you feel it immediately. That’s because the benefits often show up in day-to-day collaboration as well as in engineering metrics.
Here are some specific benefits that teams see when they improve their bug management process:
Reduced rework with clearer, more complete bug reports
Clear bug reports save time. That’s because when submissions include consistent context—like steps to reproduce, expected versus actual behavior, screenshots, and environment details—you’ll spend less time chasing missing information.
To help you create clearer reports, you can use tools like Notion that provide structured bug tracker templates and AI-assisted summaries to help you standardize reports without adding overhead. Notion AI can also flag missing details, rewrite unclear descriptions, or summarize long threads into actionable next steps, which reduces rework before it starts.
Faster triage by removing duplicates and noise
According to a paper from the Association for Computing Machinery, roughly 42 percent of bug reports are duplicates. Triage often slows down when you have to manually scan for these duplicates or decipher vague reports.
The solution? AI-assisted deduplication.
AI can identify similar bugs based on descriptions, metadata, or historical issues and help you merge reports so you can focus on what actually matters. As a result, triage meetings become shorter, more focused, and easier to run.
Improved engineering velocity with better prioritization
Because bugs often compete with features for attention, effective bug management requires you to base decisions on impact, not volume. When you clearly define severity and priority in this way, your engineering team can then make smarter trade-offs.
Connected tools also make it easier to see bugs in the context of roadmaps, sprints, and long-term goals so you can improve velocity without sacrificing quality.
Smoother, more predictable releases
Late-breaking bugs are a common root cause of delayed releases. But with better visibility into open issues, their severity, and their readiness, you can plan releases with confidence.
To do this, you’ll want to link bugs to releases and milestones. This helps everyone—from engineering and product to leadership—understand what’s blocking progress and what you’ve already resolved.
Increased visibility across teams and systems
Bug management isn’t just an engineering concern. Support teams also need to know what’s fixed, product teams need to understand user impact, and design teams need insight into usability issues.
To provide this level of clarity, a connected system makes bug status, ownership, and progress visible across teams, and real-time notifications keep everyone on the same page.
How do tools support effective bug management?
A bug and issue tracking template in Notion (Source)
Modern bug management isn’t about rigid systems—it’s about flexible capabilities that adapt to how your teams actually work. In fact, according to a paper from the International Research Journal on Advanced Engineering and Management, bug tracking tools are no longer static repositories but living systems that can help teams improve their software quality and overall efficiency.
Here’s what to look for in bug tracking software—and how a centralized workspace can support you in doing so:
Centralized capture and context
Whether a bug originates in customer feedback or quality assurance testing, it should land in a centralized bug tracking system that captures all relevant context, including descriptions, attachments, discussions, and related work.
A connected workspace like Notion makes this process easy by allowing you to collect bugs through shared databases, forms, or integrations—all while keeping context linked and accessible. That way, instead of chasing information, you can ensure that everything lives together.
AI-assisted triage and deduplication
As bug volume grows, manual triage often becomes a bottleneck. AI tools can help here by accomplishing these tasks:
Identifying potential duplicates
Suggesting severity based on historical patterns
Streamlining debugging assignments
Summarizing long reports or discussions
Highlighting related bugs or past fixes
But AI doesn’t replace human judgment. Instead, AI supports it, which allows you to spend less time sorting and more time solving.
Flexible workflows that adapt to engineering rituals
No two teams run bug management in the same way. Some triage daily, while others do it weekly. Some treat bugs like backlog items and others like interrupts.
Overall, bug tracking tools should adapt to existing rituals, not force you into rigid workflows. That’s why custom statuses, views, and automation reflect how work actually happens—whether that’s sprint-based, Kanban-style, or somewhere in between.
Integrated work across tools that engineers already use
Bug management shouldn’t exist in isolation. Instead, bugs need to connect to tasks, sprints, releases, and documentation.
A connected workspace integrates these pieces so engineers don’t have to jump between systems or sync updates manually. Then, when they fix a bug, that information flows automatically to related work, which keeps everyone aligned.
Visibility and reporting across teams
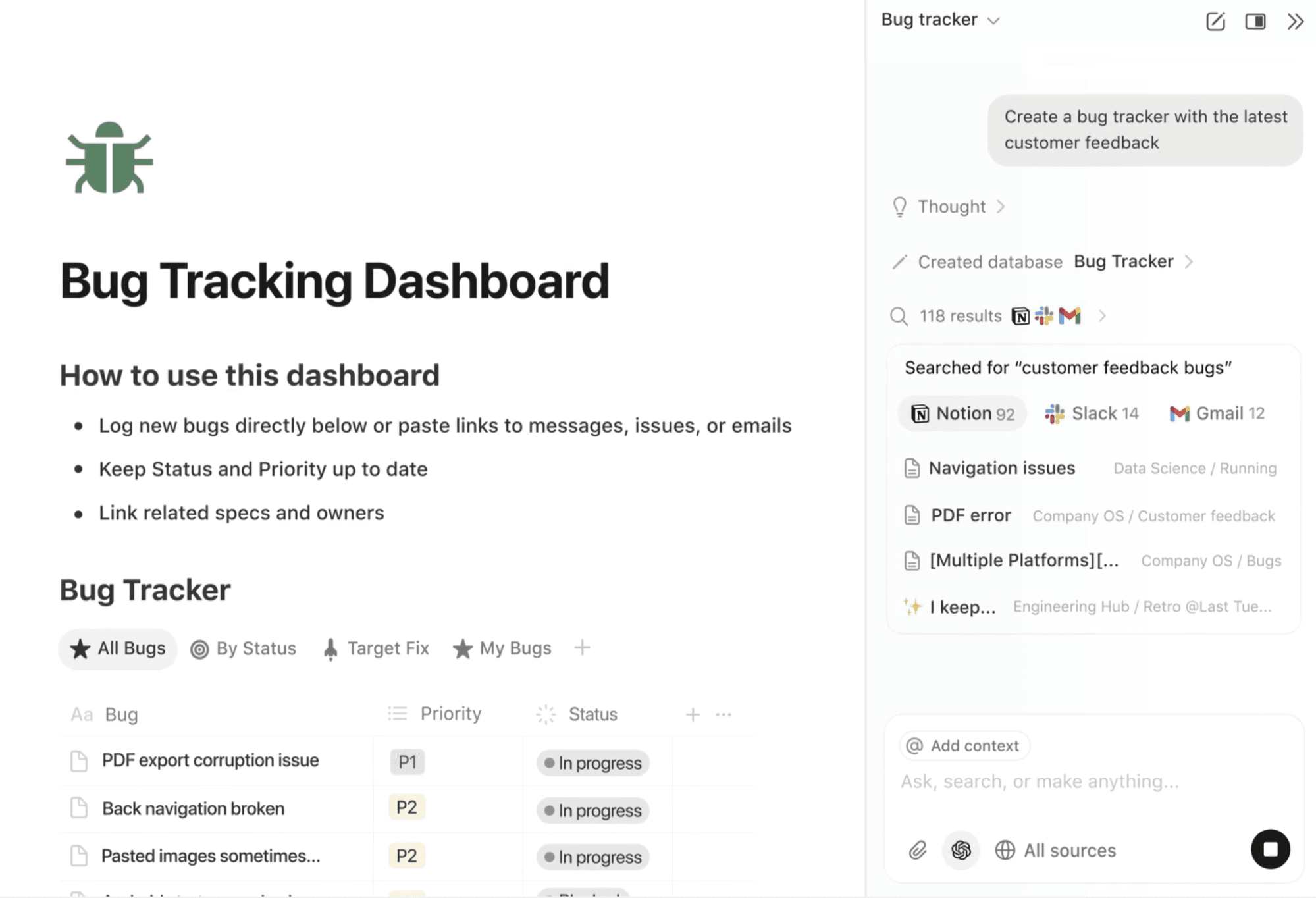
A Notion AI-generated bug tracking dashboard with the latest customer feedback (Source)
Successful bug management requires transparency, which means teams need to answer questions like these:
“How many critical bugs are open?”
“What’s blocking the next release?”
“Are we seeing recurring issues in a specific area?”
Custom dashboards, filtered views, and AI-generated summaries make this information easy to access and share without manual reporting.
What should your bug management workflow include?
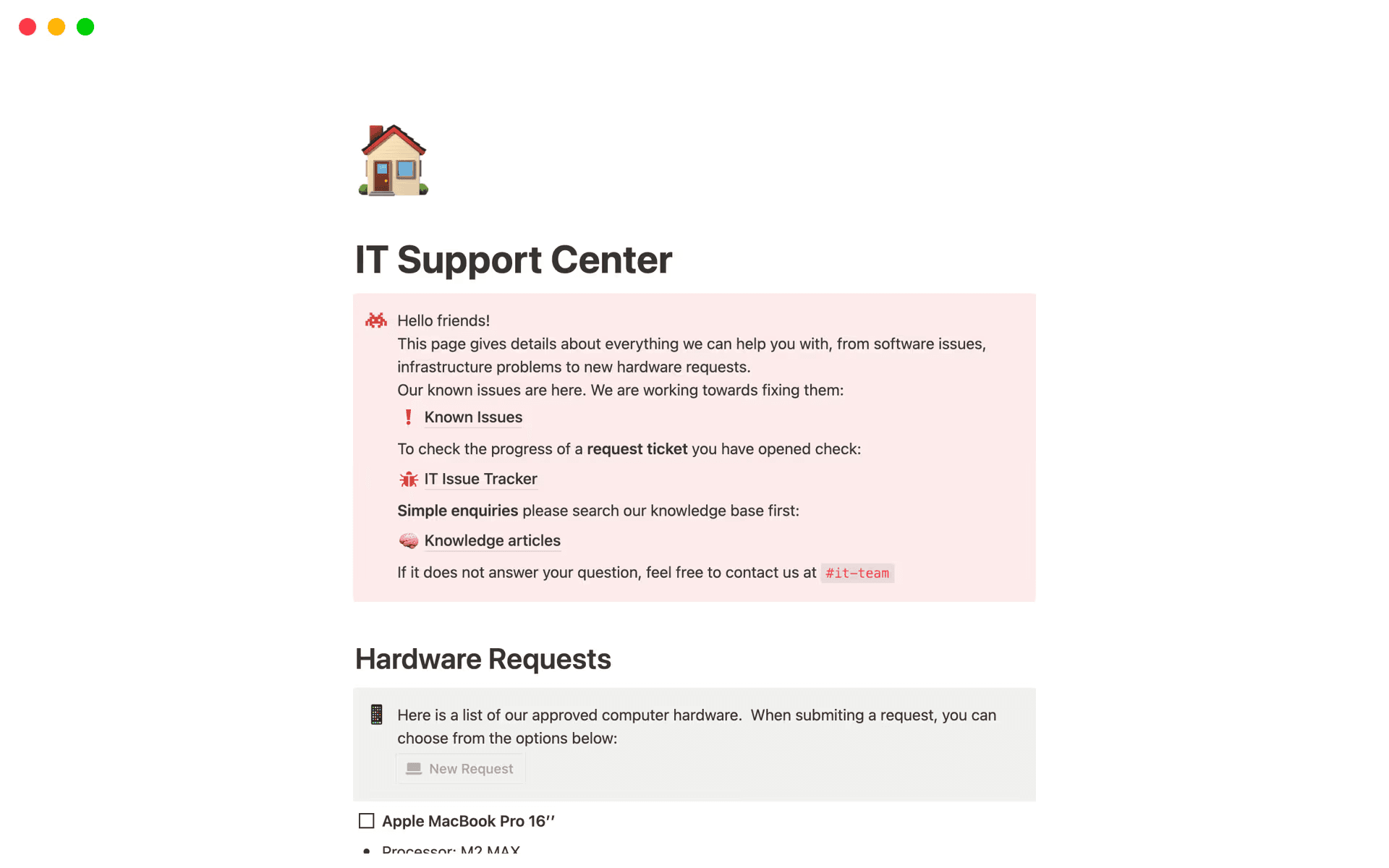
A support center and issue tracker template in Notion (Source)
Tools matter, but workflows matter just as much. That’s why the best systems combine structure with flexibility to give you clarity without unnecessary process.
Overall, a strong bug management workflow aligns engineering metrics, shared context, and cross-functional collaboration. Here’s what that looks like in practice:
Clear bug submission guidelines
Good bug management starts at the point of entry. Here, clear guidelines help testers and users know what information to include when they report issues, which reduces back-and-forth dialogues and incomplete submissions.
To help with this, you can use these Notion bug tracking templates or this super simple tracking template to standardize inputs. AI can also help you rewrite or enhance reports to ensure clarity and completeness.
Check out the video below for a tutorial on how to use Notion forms with custom fields to create a standardized bug submission process:
Uh-oh! It looks like your ad blocker is preventing the video from playing.
Please watch it on YouTube
Severity and priority definitions that everyone can follow
Severity and priority should mean the same thing to everyone, which means you need documented definitions and examples to help team members make consistent decisions. When these definitions live alongside the bug database, they’re easier to reference and apply.
AI can assist here by suggesting severity based on past bugs, impact patterns, or keywords so your teams can stay consistent as you scale.
A structured triage process with owners and timelines
Triage shouldn’t feel chaotic. That’s why a structured process is so important—it involves assigning ownership, setting expectations, and defining timelines for decision-making. The key is clarity, whether that’s via a weekly triage meeting or an asynchronous review.
Connected tools also make it easy to track ownership, due dates, and decisions so your teams don’t miss anything.
A linked system that connects bugs, tasks, sprints, and releases
Linking bugs to related tasks, sprints, and releases provides your teams with critical context. For example, engineers can see how fixes fit into broader plans, and stakeholders can track progress without interrupting the team. This linkage also enables better reporting and forecasting, which turns bug data into planning insights.
A process for learning from recurring patterns
The most overlooked part of bug management is learning.
Recurring bugs often point to deeper issues, such as unclear requirements, fragile code, or gaps in software testing. But by tagging, grouping, and analyzing bugs over time, you can identify patterns and take preventive action.
AI can also surface trends automatically to help you focus on long-term improvements rather than short-term fixes.
Start improving bug management with Notion AI
Effective bug management is about more than just tracking issues. Instead, it involves creating a system where context is connected, decisions are clear, and teams can learn as they go.
To accomplish this, Notion’s connected workspace brings bugs, tasks, documentation, and discussions together in one place. And with AI assisting triage, summaries, deduplication, and insights, bug management becomes faster, clearer, and more scalable—without adding process overhead.
If your team is ready to spend less time chasing bugs and more time shipping reliable software, it’s time to rethink how your tools support the process. Try Notion AI for free to learn how you can clean up your reports, cut noise, and link every issue to the right context.


